Scope in AngularJS
The $scope in an AngularJS is a built-in object, which contains application data and methods. You can create properties to a $scope object inside a controller function and assign a value or function to it.
The $scope is glue between a controller and view (HTML). It transfers data from the controller to view and vice-versa.
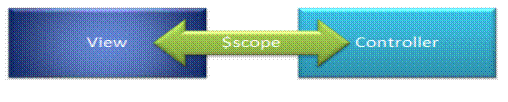
As we have seen in the controller section, we can attach properties and methods to the $scope object inside controller function. The view can display $scope data using an expression, ng-model, or ng-bind directive, as shown below.
Example: $scope
<html >
<head>
<title>AngualrJS $scope object</title>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="myNgApp">
<div ng-controller="myController">
Message: <br />
{{message}}<br />
<span ng-bind="message"></span> <br />
<input type="text" ng-model="message" />
</div>
<script>
var ngApp = angular.module('myNgApp', []);
ngApp.controller('myController', function ($scope) {
$scope.message = "Hello World!";
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Note:- The ng-model directive is used for two-way data binding. It transfers the data from controller to view and vice-versa. An expression and ng-bind directive transfers data from controller to view but not vice-versa.
To make a controller in AngularJS, you have to pass the $scope object as an argument.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.name = "Vision";
});
</script>
<p>The property "name" was made in the controller, and can be referred to in the view by using the {{ }} brackets.</p>
</body>
</html>
Understanding the Scope
If we consider an AngularJS application to consist of:
- View, which is the HTML.
- Model, which is the data available for the current view.
- Controller, which is the JavaScript function that makes/changes/removes/controls the data.
Then the scope is the Model.
The scope is a JavaScript object with properties and methods, which are available for both the view and the controller.
Example
If you make changes in the view, the model and the controller will be updated:
<html>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
<input ng-model="name">
<h1>My name is {{name}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.name = "Vision Computers";
});
</script>
<p>When you change the name in the input field, the changes will affect the model, and it will also affect the name property in the controller.</p>
</body>
</html>
$rootScope:
An AngularJS application has a single $rootScope. All the other $scope objects are child objects.
The properties and methods attached to $rootScope will be available to all the controllers.
The following example demonstrates the $rootScope and $scope object.
Example: $rootScope & $scope
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>AngualrJS Controller</title>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="myNgApp">
<div ng-controller="parentController">
Controller Name: {{controllerName}} <br />
Message: {{message}} <br />
<div style="margin:10px 0 10px 20px;" ng-controller="childController">
Controller Name: {{controllerName}} <br />
Message: {{message}} <br />
</div>
</div>
<div ng-controller="siblingController">
Controller Name: {{controllerName}} <br />
Message: {{message}} <br />
</div>
<script>
var ngApp = angular.module('myNgApp', []);
ngApp.controller('parentController', function ($scope, $rootScope) {
$scope.controllerName = "parentController";
$rootScope.message = "Hello VisionCompters!";
});
ngApp.controller('childController', function ($scope) {
$scope.controllerName = "childController";
});
ngApp.controller('siblingController', function ($scope) {
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Other RootScope Example
<html>
<head>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="myApp">
<p> The rootScope's favorite courses: </p>
<h1>{{course}}</h1>
<div ng-controller="myCtrl">
<p>PHP is a server-side scripting language designed primarily for web development but also used as a general-purpose programming language. Originally created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994, the PHP reference implementation is now produced by The PHP Development Team.</p>
<h1>{{course}}</h1>
</div>
<p>The rootScope's favorite course is still:AngularJS (commonly referred to as "Angular" or "Angular.js") is a complete JavaScript-based open-source front-end web application framework mainly maintained by Google and by a community of individuals and corporations to address many of the challenges encountered in developing single-page applications.</p>
<h1>{{course}}</h1>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.run(function($rootScope) {
$rootScope.course = 'PHP';
});
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.course = "AngularJs";
});
</script>
<p>Notice that controller's course variable does not overwrite the rootScope's course value.</p>
</body>
</html>
As per the above example, properties added in $rootScope are available in all the controllers.
The $scope object contains various methods. The following table lists important methods of $scope object.
Method |
Description |
$new() |
Creates new child scope. |
$watch() |
Register a callback to be executed whenever model property changes. |
$watchGroup() |
Register a callback to be executed whenever model properties changes. Here, specify an array of properties to be tracked. |
$watchCollection() |
Register a callback to be executed whenever model object or array property changes. |
$digest() |
Processes all of the watchers of the current scope and its children. |
$destroy() |
Removes the current scope (and all of its children) from the parent scope. |
$eval() |
Executes the expression on the current scope and returns the result. |
$apply() |
Executes an expression in angular outside the angular framework. |
$on() |
Register a callback for an event. |
$emit() |
Dispatches the specified event upwards till $rootScope. |
$broadcast() |
Dispatches the specified event downwards to all child scopes. |
$watch:
Angular scope object includes $watch event which will be raised whenever a model property is changed.
Example:
<html>
<head>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="myNgApp">
<h2>Example of watch</h2>
<div ng-controller="myController">
Enter Message: <input type="text" ng-model="message" /> <br />
New Message: {{newMessage}} <br />
Old Message: {{oldMessage}}
</div>
<script>
var ngApp = angular.module('myNgApp', []);
ngApp.controller('myController', function ($scope) {
$scope.message = "Hello D.G.Prasad!";
$scope.$watch('message', function (newValue, oldValue) {
$scope.newMessage = newValue;
$scope.oldMessage = oldValue;
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Note:- As you can see in the above example, $watch registers a callback, which will get called whenever the specified model property "message" changes.
For
More Explanation
&
Online Classes
More Explanation
&
Online Classes
Contact Us:
+919885348743
+919885348743
