Controllers
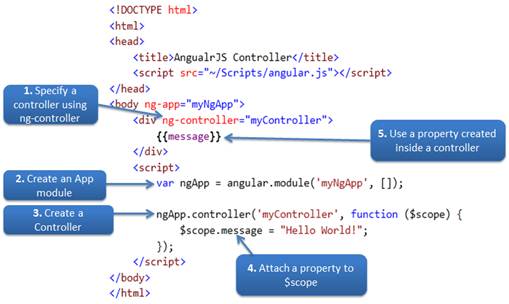
AngularJS controllers are used to control the flow of data of AngularJS application. A controller is defined using ng-controller directive. A controller is a JavaScript object containing attributes/properties and functions. Each controller accepts $scope as a parameter which refers to the application/module that controller is to control.
AngularJS Controller Example
The following example demonstrates attaching properties to the $scope object inside a controller and then displaying property value in HTML.
Example: AngularJS Controller.
Minification Syntax:
All the script files in AngularJS application should be minified in the production environment.
The minification process shortens parameter and function names. As mentioned before, AngularJS controller function may include $scope or other parameters. If minification process changes the parameter names then AngularJS application will break because Angular framework needs the same parameter name for built-in objects such as $scope. Use the following syntax so that minification will not change the parameter name.
<html >
<head>
<title>AngualrJS Controller</title>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="myNgApp">
<div ng-controller="myController">
{{message}}
</div>
<script>
var ngApp = angular.module('myNgApp', []);
ngApp.controller('myController', function ($scope) {
$scope.message = "Hello World!";
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Note: AngularJS framework injects $scope object to each controller function. It also injects other services if included as a parameter of controller function.
Practice Examples:
<html>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<body>
<h2>AngularJs-Controller</h2>
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
First Name: <input type="text" ng-model="firstName"><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" ng-model="lastName"><br>
<br>
Full Name: {{firstName + " " + lastName}}
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.firstName = "Vision";
$scope.lastName = "Computers";
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation
- Here, the AngularJS application runs inside the <div> is defined by ng-app="myApp".
- The AngularJS directive is ng-controller="myCtrl" attribute.
- The myCtrl function is a JavaScript function.
- AngularJS will invoke the controller with a $scope object.
- In AngularJS, $scope is the application object (the owner of application variables and functions).
- The controller creates two properties (variables) in the scope (firstName and lastName).
- The ng-model directives bind the input fields to the controller properties (firstName and lastName).
AngularJS controller example with methods (variables as functions)
<html>
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="personCtrl">
First Name: <input type="text" ng-model="firstName"><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" ng-model="lastName"><br>
<br>Full Name: {{fullName()}}
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('personCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.firstName = "Vision";
$scope.lastName = "Computers";
$scope.fullName = function() {
return $scope.firstName + " " + $scope.lastName;
};
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
For
More Explanation
&
Online Classes
More Explanation
&
Online Classes
Contact Us:
+919885348743
+919885348743
